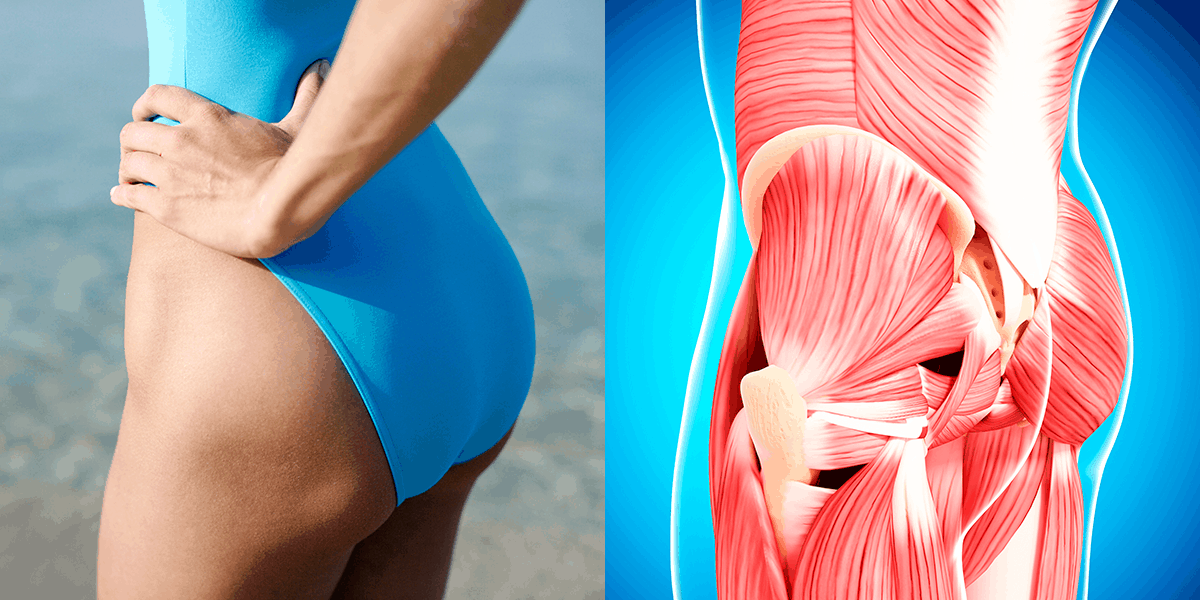
The Most Common Mistake That Makes People Look Fat
The answer. Tight hip flexor muscles cause the abdominal muscles to pooch out. Making you look fat, but its truly just muscle tightness.
What tight muscles cause this?
Your hips are the bridge between your upper body and lower body. They are at the core of your body’s movement.
Sitting within the well of your hip and lower spine is the psoas major muscle, one of the two muscles that comprise the iliopsoas.
It’s commonly called the “mighty” psoas (pronounced so-az) for the many important functions it contributes in the movement of your body.
The psoas is the only muscle in the human body connecting the upper body to the lower body.
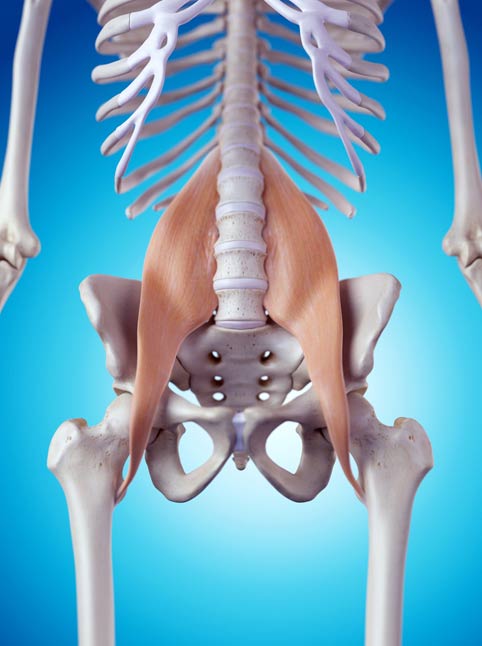
This muscle attaches to the vertebrae of the lower spine, moves through the pelvis and connects to a tendon at the top of the femur.
It also attaches to the diaphragm, so it’s connected to your breathing, and upon it sits all the major organs.
A functioning psoas muscle provides a neutral pelvic alignment, stabilizes the hips, supports the lower spine and abdomen, supports the organs in the pelvic and abdominal cavity and gives you greater mobility and core strength.
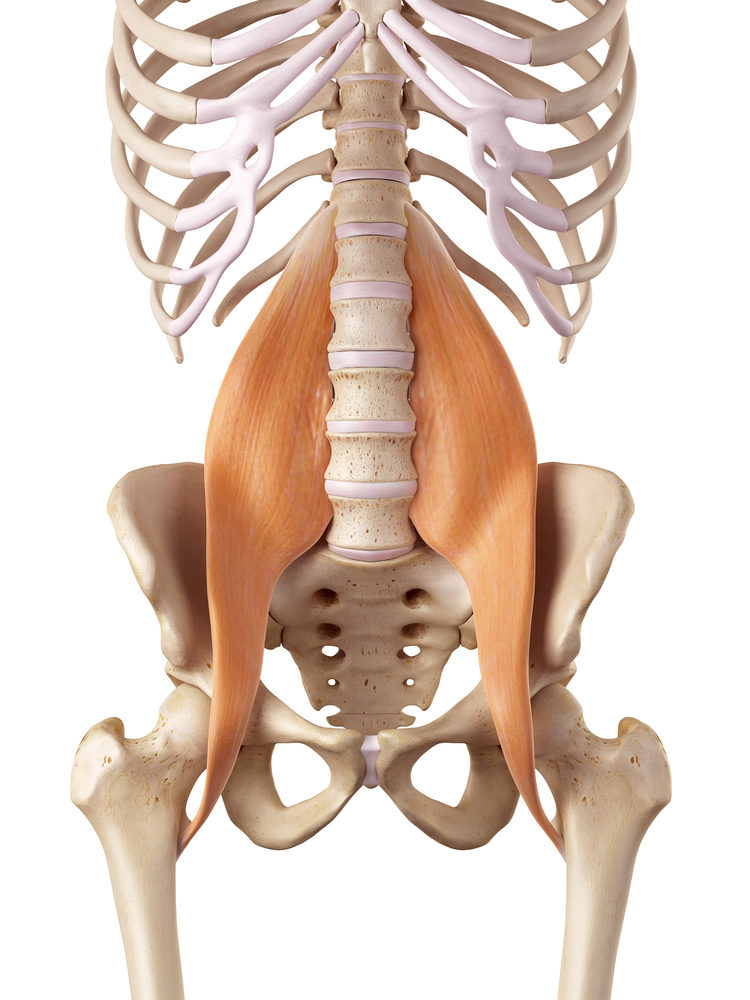
When it functions well, it has the ability to…
… help you achieve peak performance day after day.
… rapidly drop ugly body fat that stubbornly clings to your body.
… train harder, heavier and gain strength faster than ever before.
… hit your peak of intimacy health and performance.
… flood your mind and body with renewed energy and vigor.
Simply, this muscle is the core of activity in your body.
So, when it’s out of balance or if the psoas tightens, which causes serious consequences which flow throughout the body. Which is why I encourage you to try to perform necessary stretches and positions.

This tightness is potentially making you look like you’re at least 5-7% higher body fat than you actually are.
It tends to create a lower belly bulge, love handles that don’t belong, and can actually lead to low back pain when left untreated.
Tight Hip Flexors directly affects emotions, neurological balance, and confidence.
Interestingly, it has a huge effect, and when unrecognized can lead to sadness, depression, anxiety, or lack of will-power.

Unlock your abs, get rid of love handles, feel more self-confident, and get rid of old emotional baggage; by increasing hip flexibility.
Are your hips tight?
Pain & discomfort from tight hips is felt in the upper groin area.
Tight hips lead to issues in the low back, knees, and sacroiliac joints. It’s common to experience lower back pain or hamstring strains.
Tight hips often lead to issues in the low back, knees, and sacroiliac joints.
A simple way to test flexibility of the hip flexor muscles is called the Thomas test:
- Lie on your back on the floor, a bench, or another stable, flat surface.
- Bring both knees to your chest.
- Hold your right knee against your chest.
- Straighten your left leg.
- Lower your left leg as far as possible.
- Repeat with the other leg.
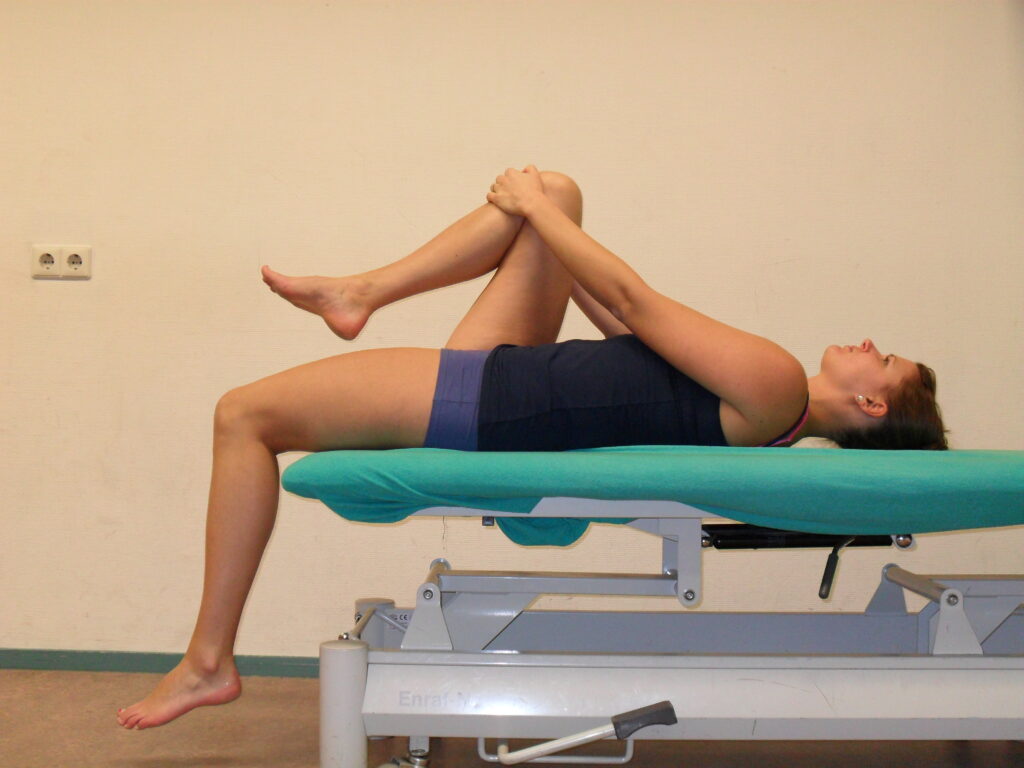
Hip flexors are considered tight if either leg cannot completely lower to the surface you are lying on.
Cause of tight hips?
An inactive lifestyle leads to tight hip flexors and hip flexor pain. Which is because excessive sitting causes the muscles to relax and deactivate.
They become progressively weaker and shorter, commonly causing a painful condition called adaptive shortening.
5 Ways to Tell If You Have a Psoas Muscle Imbalance
When you have a tight psoas muscle, you may experience pain in your lower back or in your hips, specifically when elevating your legs. This is caused by the muscle compressing the discs in the lumbar region of your back. Stretching your muscles and releasing the tension on the psoas is the best way to keep this from happening. It takes time and daily attention to keep your psoas muscles relaxed, stretched, and strong.
While most people with psoas issues have tight psoas muscles, there are some people whose psoas muscles can be overstretched. In this case, if you stretch your psoas and it is already overstretched, you will cause increased problems.
Here are 5 ways to test if you have a psoas muscle imbalance:
Leg length discrepancy. A tight psoas muscle will cause your pelvis to rotate forward. Which can cause an internal rotation of your leg on the affected side. The opposite leg will rotate externally in an effort to counterbalance. This will make the affected leg longer so that every time you take a step, it drives your leg up into your hip socket. This can lead to functional leg length discrepancy.
Knee and low back pain. If you experience random knee or low back pain, it may be coming from your psoas muscles, causes your femur to in be locked into your hip socket & rotation in the joint can’t occur. This can torque your knee and low back.
Postural problems. A shortened psoas muscles can pull your pelvis into an anterior tilt, compressing the spine and pulling your back into hyperlordosis or “duck butt.” If your psoas is overstretched or weak, it can flatten the natural curve of your lumbar spine, creating a “flat butt.” Which can cause a low-back injury, especially at the intervertebral discs. You could feel pain at the front of your hip as well.
Difficulty moving your bowels. A tight psoas muscle can lead to or even result in constipation. Your torso shortens, decreasing the space for your internal organs. Which then affects food absorption and elimination.
Menstrual cramps. A muscle imbalance in your psoas can be partly responsible for menstrual cramps, as it puts increased pressure on your reproductive organs.

Tight hips may also be caused by:
- standing after long periods of sitting
- a tipped pelvis, which creates a structural imbalance
- postural habits like leaning over into one hip or leaning forward into both hips when standing
- sleeping all night on the same side of the body
- having one leg longer than the other
Tight hips may also flare up when you perform lower body exercises, including squats and dead lifts.

Things to prevent or reduce your risk for tight hips?
It may not be possible to prevent hip tightening all together, but you can reduce your risk for hip pain by:
- Get up and move around every hour or so if you sit at a desk for long periods of time.
- Warm up properly before any workout.
- Stretch at the end of every workout.
Here’s a great hip flexor stretch that you should do daily, especially after a workout, but should be done consistently in between.
Perform 3 times and hold for 60 seconds each time. Each leg. Perform daily.
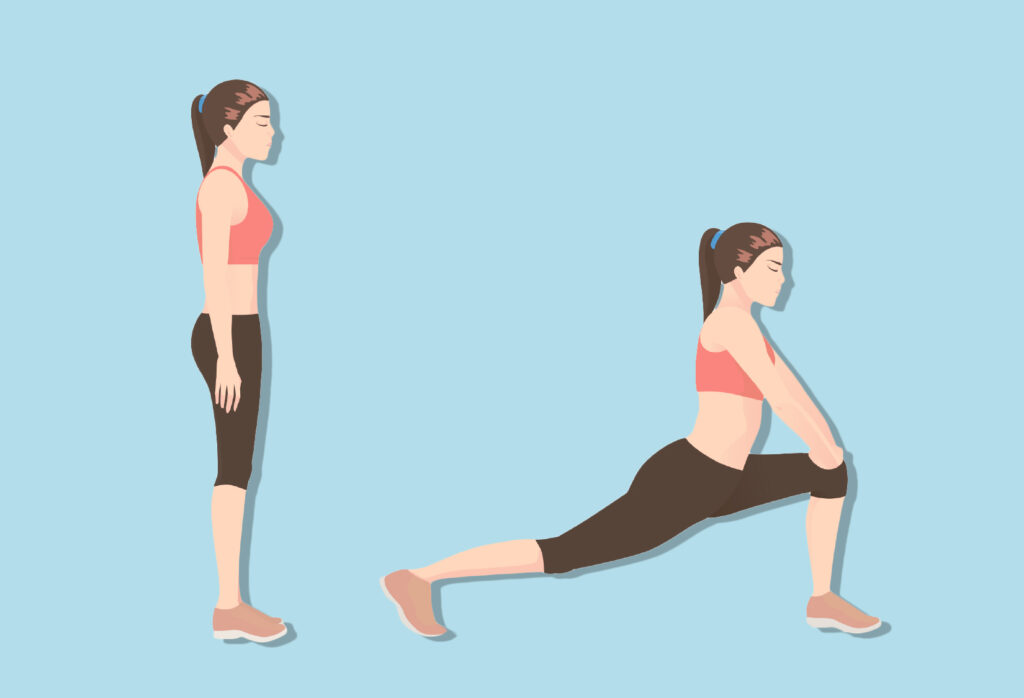
Your hip flexors are a set of muscles located at the top of your thighs that are major components in moving your lower body.
They allow you to walk, kick, bend, and rotate your hips. But if your muscles are too rigid & tight went you make a quick movement, your hip flexors can result in a pull or tear.
A hip flexor strain could cause mild discomfort or be so severe that you have difficulty walking coupled with muscle spasms and a lot of pain.
Daily stretches can assist in keeping your hip flexors loose and prevent injuries.


The Air Ducts
September 20, 2023 at 1:13 amYou helped me a lot with this post. I love the subject and I hope you continue to write excellent articles like this.
Hairstyles
September 26, 2023 at 4:19 amYour articles are extremely helpful to me. Please provide more information!